Product Catalog
Featured Products
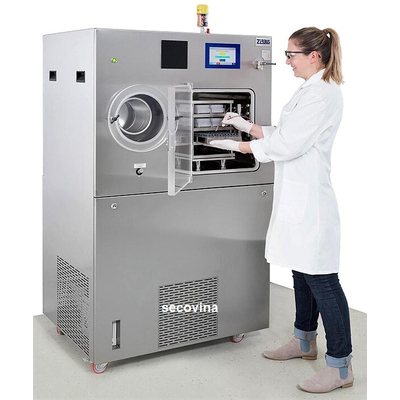
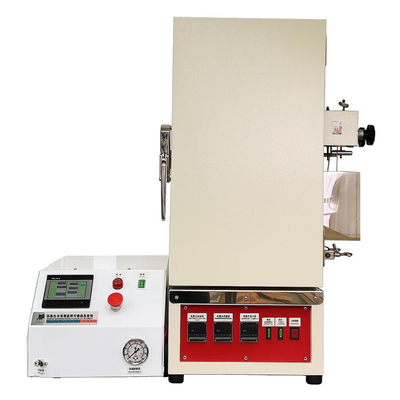
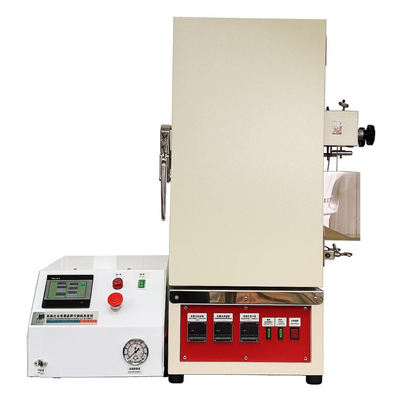
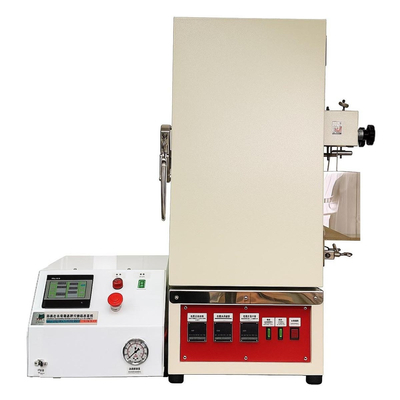
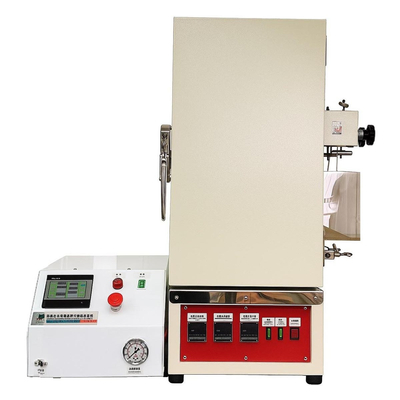
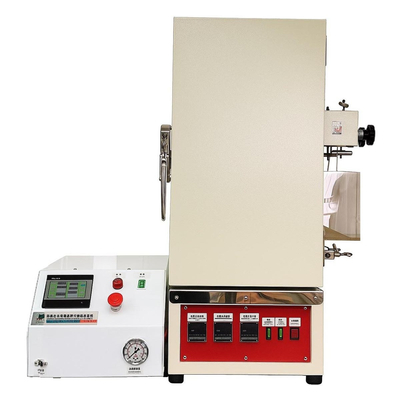
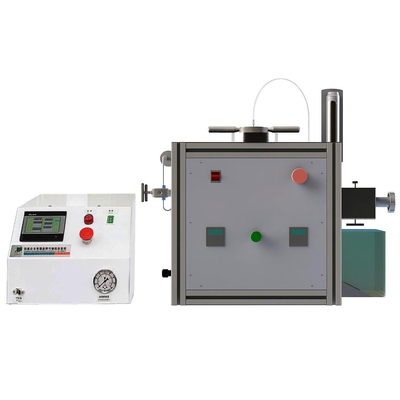
Laboratory Freeze Dryer
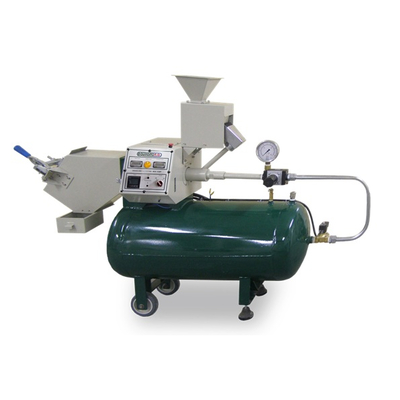
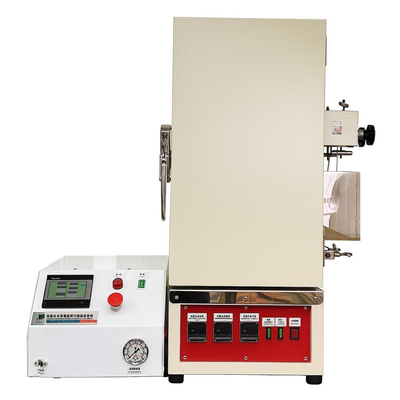
Gravelometer / Stone Chip Resistance Test
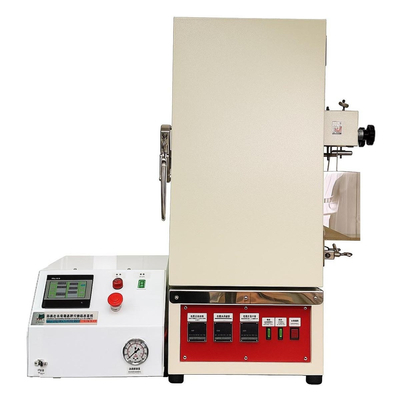
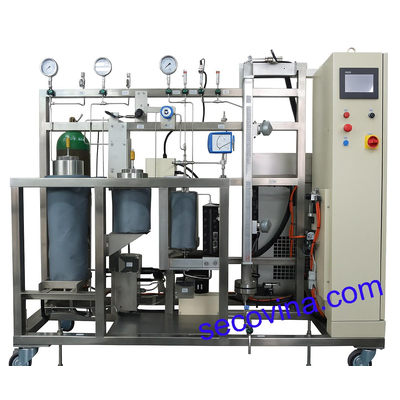
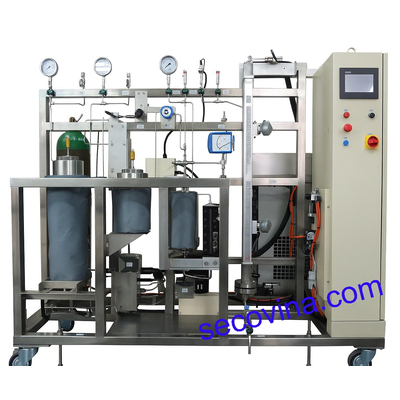
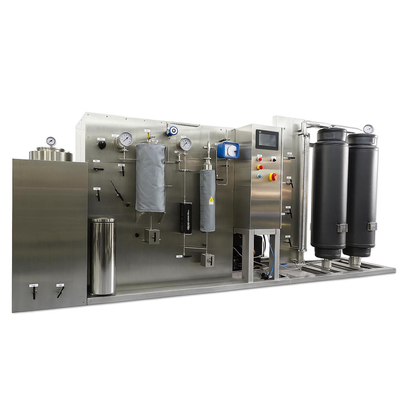
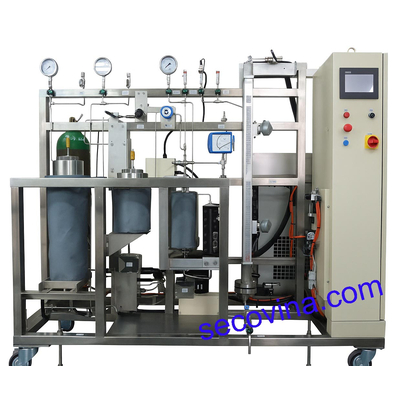
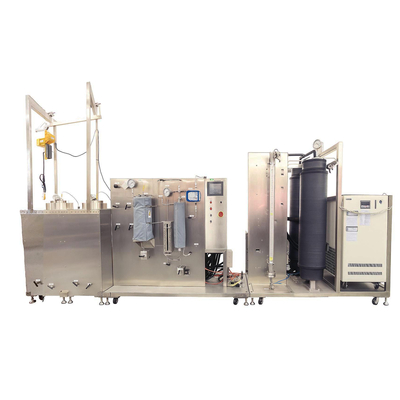
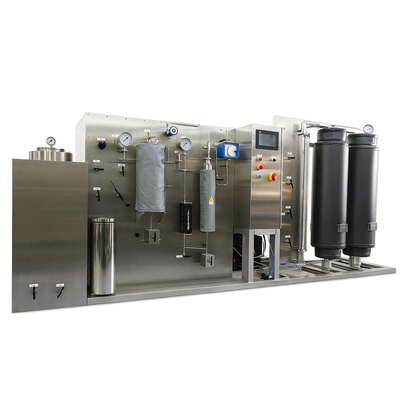
Supercritical Fluid Extraction
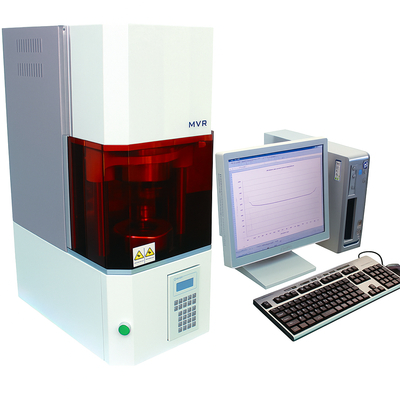
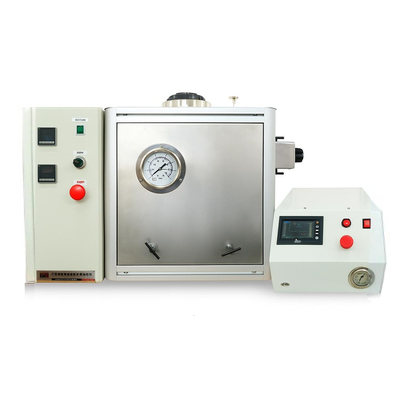
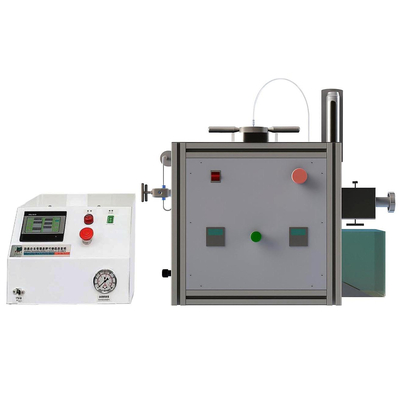
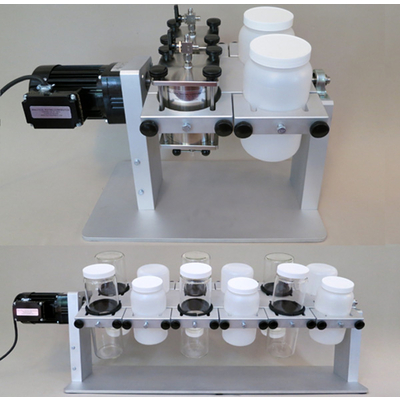
Mooney Viscometer
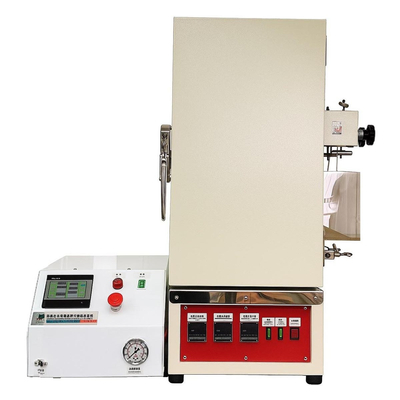
Flat Die Rheometer (FDR)
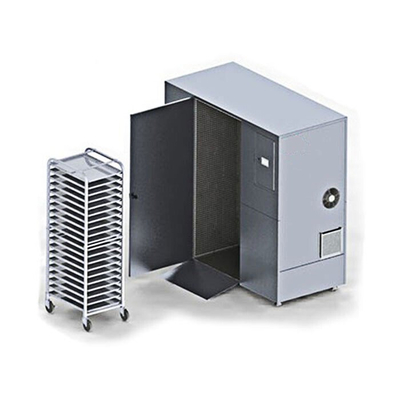
Cyclic Corrosion Test CORR Auto
Các ứng dụng của CO2 siêu tới hạn
Fanpage
Website Traffic
- Đang online 0
- Hôm nay 0
- Hôm qua 0
- Trong tuần 0
- Trong tháng 0
- Tổng cộng 0
INDUSTRY NEWS
Supercritical CO2 Extraction
Supercritical CO2 Extraction
Supercritical CO₂ – Advances in Green Chemistry
Supercritical CO₂ – Advances in Green Chemistry
Heat Pump Dehydrators
Heat Pump Dehydrators
Fractionated extraction of saponins from Vietnam ginseng using supercritical CO2, ethanol
Fractionated extraction of saponins from Vietnam ginseng using supercritical CO2, ethanol
Aerogel - Materials of the century
Aerogel is a synthetic porous ultralight material derived from a gel, in which the liquid component for the gel has been replaced with a gas. The result is a solid with extremely low density and low thermal conductivity. Nicknames include frozen smoke, solid smoke, solid air, solid cloud, blue smoke owing to its translucent nature and the way light scatters in the material. It feels like fragile expanded polystyrene to the touch. Aerogels can be made from a variety of chemical compounds.
Water Activity (aw) in Foods
Water Activity (aw) in Foods
Selective Extraction of Fatty Acids and Carotenoids from Microalgae by Supercritical Fluid Systems
Selective Extraction of Fatty Acids and Carotenoids from Microalgae by Supercritical Fluid Systems Spirulina maxima, a type of microalgae, is of great interest to the cosmetic, food, and pharmaceutical industries due to its chemical composition. The blue-green cyanobacterium is a source of carotenoids, which are rich in Vitamin A and act as powerful antioxidants.
Micro Algae | Uses for Supercritical Fluids
Supercritical fluid extraction is an environmentally clean technology using carbon dioxide to isolate a variety of natural compounds from micro algae. This benign extraction process provides: - high selectivities - short extraction times - leaves no toxic solvent residues in the extract
Aerogels | Uses for Supercritical Fluids
High temperature conversion of a liquid organic solvent to the supercritical state with subsequent venting Liquid CO2 displacement of an organic solvent with subsequent supercritical CO2 venting Supercritical CO2 extraction of an organic solvent at low temperatures
Nutraceuticals | Uses for Supercritical Fluids
Compared to traditional extraction methods, natural supercritical CO2 extraction has many benefits and is Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS). Supercritical CO2 extraction eliminates exposure of the natural product to oxygen during the process and thus reduces oxidation of sensitive bioactive compounds. It also is a low temperature operation that does not promote thermal degradation of sensitive nutraceutical compounds . In addition, when the supercritical CO2 extract is depressurized, there are
Natural rubber latex concentrate -Specifications-tcvn 6314:2013
Natural rubber latex concentrate – Centrifuged or creamed, ammonia – preserved types – Specifications (TCVN 6314:2013 - ISO 2004:2010)
Foods | Uses for Supercritical Fluids
Extraction of hops for beer production Decaffeination of coffee and tea Nicotine/tar-free tobacco Separation of Free Fatty Acids from vegetable oils Fractionation of Poly Unsaturated Fatty Acids from animal lipids Refining and deodorization of vegetable oils Recovery of antioxidants (vitamins E and A) Fractionation of glycerides Extraction of oil from oil-bearing materials Deoiling and purification of lecithin Decholesterolization of butter, egg, fish and meat muscle Deoiling of snack-foods Spic
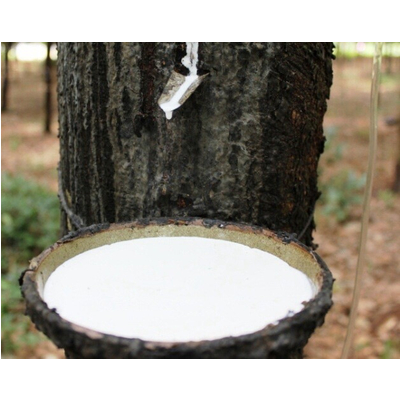
Method for producing deproteinized natural rubber latex
1. A method for deproteinizing natural rubber latex comprising steps of: adding a urea denaturing agent for proteins and a surfactant to raw natural rubber latex; transporting the mixture through a fluid channel while agitating and mixing to denature proteins in raw natural rubber latex; and separating and removing the denatured proteins resulted from the previous step. 2. The method according to claim 1, wherein the urea denaturing agent for proteins is used in the form of a 0.01% to 1% by wei
Enzyme-assisted supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of black pepper oleoresin for enhanced yield of piperine-rich extract
Piperine, along with its isomer chavicine, is the alkaloid[1] responsible for the pungency of black pepper and long pepper. It has also been used in some forms of traditional medicine and as an insecticide.
Astaxanthin extraction in H. pluvialis by Supercritical carbon dioxide
astaxanthin từ H. pluvialis by Supercritical carbon dioxide
Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of Gac oil.
Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of Gac oil.
Supercritical fluid extraction of cordycepin and adenosine from Cordyceps
Supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) was used to extract cordycepin and adenosine from Cordyceps
METHOD 1311 TOXICITY CHARACTERISTIC LEACHING PROCEDURE
METHOD 1311 TOXICITY CHARACTERISTIC LEACHING PROCEDURE
Essential Oils | Uses for Supercritical Fluids
Essential oils can be primary ingredients in perfumes for cosmetics, soaps, and detergents. They form the basis of the spices in our foods. So then why the interest in extracting essential oils with supercritical CO2? Because the use of essential oils continues to be essential for modern living.
Applications of supercritical CO2
Applications of supercritical CO2
Oil extraction in plants using supercritical co2 technology
Oil extraction in plants using supercritical co2 technology
Co2 Supercritical Fluid Technology
Co2 Supercritical Fluid Technology
Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of Gac oil
Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of Gac oil
Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of Gac oil
Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of Gac (Momordica cochinchinensis Spreng) aril was performedat pressures ranging from 200 to 400 bar, temperatures from 313 to 343 K and specific flow rates from50 to 90 kg h−1CO2kg−1Gac aril. Total oil recovery and carotenes concentration were investigated inthe course of extraction. Mathematical modelling of oil solubility data was also performed. The resultsshowed that at specific flow rate of 70 kg h−1kg−1, pressure of 400 bar and temperature of 343 K